In this tutorial, we will be covering the Multiple access in the Data link layer of the OSI Model.
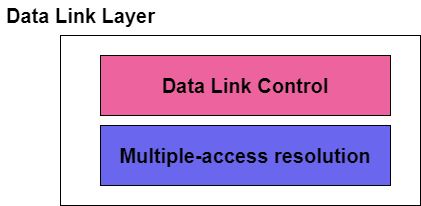
The Data link layer can be considered as two sublayers, where the upper sublayer is mainly responsible for the data link control and the lower layer is responsible for resolving the access to the shared media.
If there is a dedicated channel in that case there is no need for the lower sublayer.

The upper sublayer of the data link layer is mainly responsible for the flow control and error control and is also referred to as Logical link control(LLC); while the lower layer is mainly responsible for the multiple-access resolution and thus is known as Media Access control (MAC) layer.
The main objectives of the multiple access protocols are the optimization of the transmission time, minimization of collisions, and avoidance of the crosstalks.
Multiple Access protocols mainly allow a number of nodes to access the shared network channel. Several data streams originating from several nodes are transferred via the multi-point transmission channel.
The Multiple access protocols are categorized as follows. Let us take a look at them:

In the random access, there is no such station that is superior to another station and none is assigned control over the other.No station permits another station to send.
Each station can transmit whenever it desires on the condition that it follows the predefined procedure that includes the testing state of the medium.
Given below are the protocols that lie under the category of Random Access protocol:
While using the Controlled access protocol the stations can consult with one another in order to find which station has the rights to send the data. Any station cannot send until it has been authorized by the other stations.
The three main controlled access methods are as follows;
Channelization is another method used for multiple access in which the available bandwidth of the link is shared in the time, frequency, or through the code in between the different stations.
Three channelization protocols used are as follows;
We will cover all the above protocols in our upcoming tutorials.